Strokes happen suddenly and can cause permanent brain damage. If not treated quickly, they can kill you or leave you permanently disabled. If you think someone is having a stroke, call 911 immediately. Knowing the signs of a stroke can save a life.
What’s going on when someone has a stroke? Strokes happen in a couple of different ways. Andrew Southerland, MD, a stroke specialist at UVA Health, spoke with us about the types of strokes and what causes them.
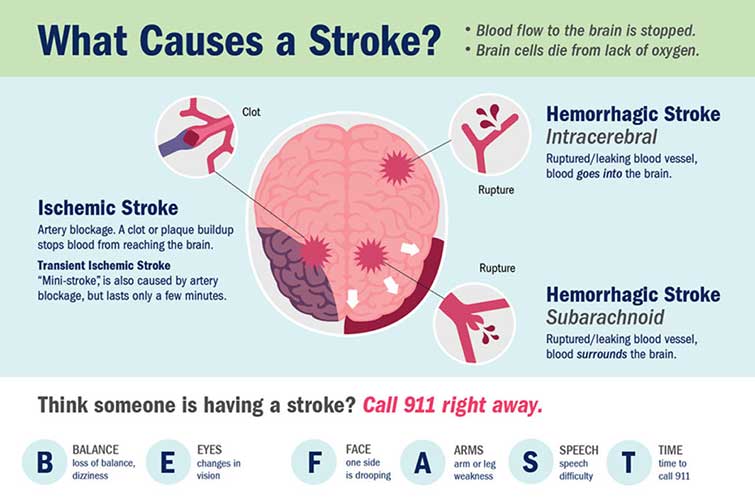
Types of Strokes: Different Causes, Same Result
There are two:
- Ischemic
- Hemorrhagic
“Both are under the umbrella of stroke, but have different treatments,” notes Southerland. “Ischemic strokes are the vast majority of strokes. Probably 80 to 85% of all the strokes we see coming into the hospital.”
These happen when a blood clot or plaque blocks an artery and keeps blood from getting to your brain. The clot or plaque can travel to the artery from a different part of your body. Without blood flow, your brain cells don’t get enough oxygen and they die.
Southerland explains all this to his patients in a way they can easily understand: “You have a clogged plumbing pipe, and we need to give you some Drāno.”
Unclogging the Pipe
If you have an ischemic stroke, you’ll get a clot-busting medicine to quickly get blood flowing again.
“It's designed to break down blood clots (or fresh thrombus, that’s the medical term),” says Southerland. “When it works, it works well enough to restore function to a part of your brain that is in the process of dying. We're trying to bring dying brain back to life.”
Ischemic vs. Hemorrhagic
Hemorrhagic strokes are less common. They happen in about 15 to 20% of stroke cases. Hemorrhagic strokes also keep your brain from getting oxygen, but in a different way.
Concerned About Stroke?
If you suspect someone is having a stroke, call 911 right away.
Talk to a UVA Health primary care doctor about preventing a stroke.
With these types of strokes, notes Southerland, “Patients get bleeding out into the brain through a ruptured blood vessel.” High blood pressure in the brain or an aneurysm can make the blood vessel rupture. An aneurysm happens when there’s a weak spot in the wall of a blood vessel. That spot can bulge out and then break. Blood leaks into your brain or into the space between your brain and skull. Oxygen can’t reach your brain cells.
Knowing the type of stroke you have is important when deciding treatment. “We need to make sure it's not a bleeding or hemorrhagic stroke before we give clot-busting medication,” says Southerland. Clot-busting medicine affects how your blood clots so can be dangerous to give to someone with a hemorrhage stroke.
What About “Mini-Strokes”?
Transient ischemic attacks, sometimes called “mini-strokes,” also happen when you have a blockage or reduced blood flow to your brain. The symptoms are very similar to a stroke, but the attacks only last a short time. A transient ischemic attack is a sign that a stroke may be in your future. It’s important to get medical help right away.
Get Help ASAP
Strokes are a leading cause of death and disability in the U.S. Anytime someone shows the signs of a stroke, you should call 911 right away. Remember stroke symptoms using BE FAST:
- Balance: loss of balance or coordination
- Eyesight: trouble with vision
- Face: drooping or loss of control
- Arm: weakness on one side
- Speech: slurred or difficulty talking
- Time: call 911 right away